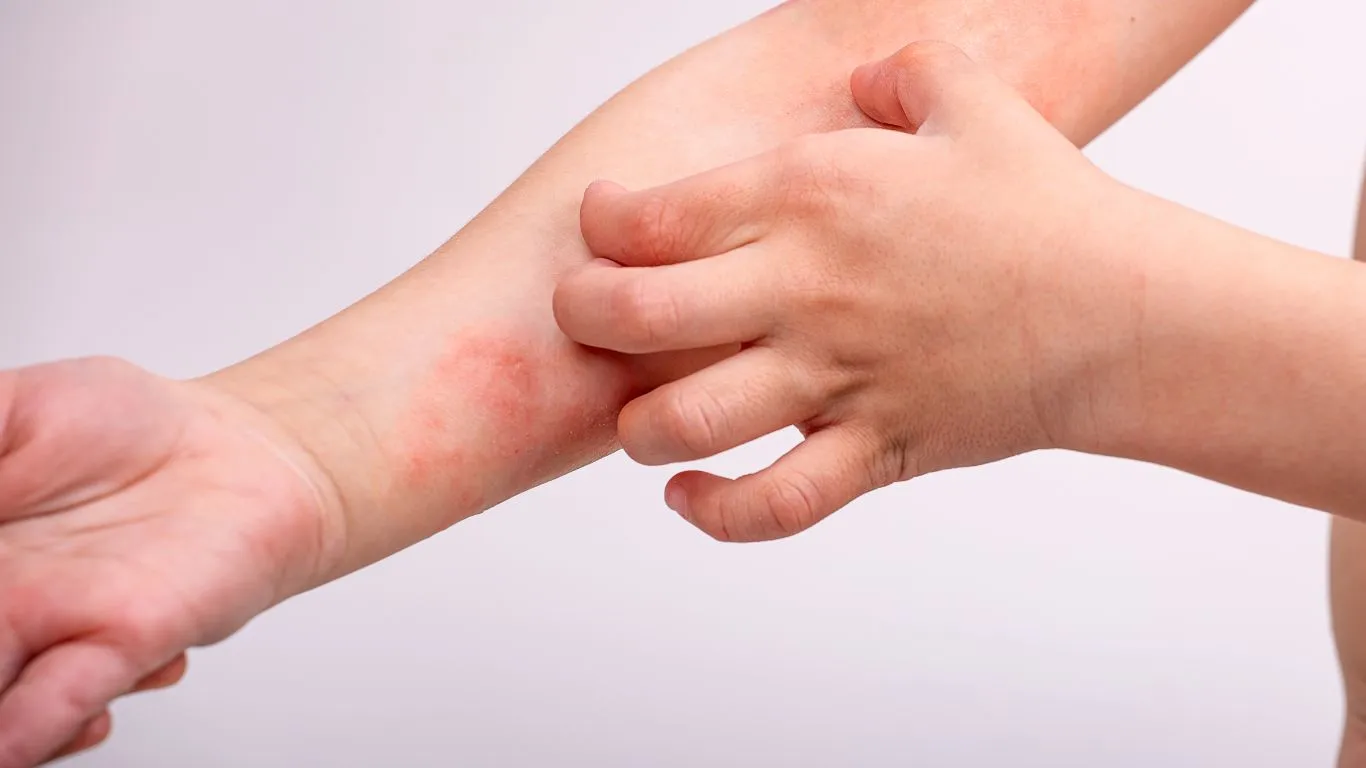
Atopic dermatitis is a common and chronic skin condition that affects many individuals, often appearing in childhood and lasting for extended periods. This condition is characterized by dry, red, and itchy skin, leading to discomfort and affecting the quality of life. Atopic dermatitis is a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors, requiring special attention.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- Red patches on the skin, particularly in areas like the face, neck, and hands.
- Intense itching, which may lead to scratching and increased inflammation.
- Dry and flaky skin.
- Over time, the skin may thicken and show signs of scratching.
- Discoloration of the skin in affected areas, especially after wounds heal.
Causes
In most cases, there may not be a specific cause for atopic dermatitis, but certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing it, including:
- Overactive Immune System: Atopic dermatitis may arise from an overactive immune response that causes dryness of the skin barrier and itching.
- Genetics: Genetic factors play a significant role; if you have family members with atopic dermatitis or other types of eczema, you may be at increased risk.
- Exposure to Irritants: Additionally, exposure to certain triggers can heighten the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis, such as:
- Prolonged exposure to dry air, extreme heat, or cold.
- Certain soaps, shampoos, body washes, and facial cleansers.
- Laundry detergents and fabric softeners.
- Fabrics like wool or polyester.
- Surface cleaners and disinfectants.
- Fragrances.
- Metals, especially nickel, in jewelry or utensils.
- Formaldehyde, found in household disinfectants, some vaccines, adhesives, and glues.
- Dust mites.
- Stress: Psychological stress can contribute to the emergence or worsening of symptoms.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during pregnancy or menstruation, can affect the condition.
Read More: Collagen Stimulating Injections
Treatment Methods
Treatment methods include:
Home Remedies
Certain tips and natural methods can help alleviate symptoms of atopic dermatitis at home, such as:
- Avoiding scratching the skin to prevent worsening the condition.
- Regularly moisturizing the skin, especially after bathing.
- Steering clear of symptom triggers.
- Using colloidal oatmeal baths to soothe the skin and promote healing.
Medications
There are a variety of medications available for treating atopic dermatitis, some of which are available over the counter:
- Antihistamines to help relieve itching.
- Corticosteroid creams to reduce inflammation and itching; more severe cases may require oral corticosteroids.
- Ruxolitinib cream, approved for patients aged 12 and older with mild to moderate atopic dermatitis.
Other Treatments
While medications are usually effective in alleviating symptoms, some individuals may require stronger treatment, especially if eczema is widespread. This may include light therapy or systemic medications.
Light therapy involves shining specific light on the affected area, where ultraviolet (UV) rays penetrate deep skin layers, helping to reduce inflammation associated with eczema.
UVB rays target the outer layers, soothing inflammation and reducing scaling and itching. The effects of light therapy are often temporary, lasting up to two months, and patients may need 6 to 8 sessions to achieve the desired benefits.
Prevention Methods
Establishing a basic skincare routine can help prevent flare-ups of eczema. Here are some tips that may help reduce dryness caused by bathing:
- Moisturize Twice Daily: Using creams and ointments, especially those containing shea butter and petroleum jelly, helps maintain skin hydration.
- Daily Bathing: It is advisable to shower or bathe daily using warm water instead of hot, ensuring the bathing duration does not exceed 10 minutes.
- Drying the Skin After Bathing: Use a soft towel and gently pat the skin dry. It is preferable to apply moisturizer while the skin is still damp, within three minutes of drying.
- Choose a Mild Cleanser: Opt for a soap-free and chemical-free cleanser, avoiding dyes, alcohol, and fragrances.
References:
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema) – Symptoms and causes. (n.d.). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atopic-dermatitis-eczema/symptoms-causes/syc-20353273
- National Eczema Association. (2024, August 22). Eczema (Atopic dermatitis): causes and treatment. https://nationaleczema.org/eczema/
- Website, N. (2024, September 11). Atopic eczema. nhs.uk. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/atopic-eczema/