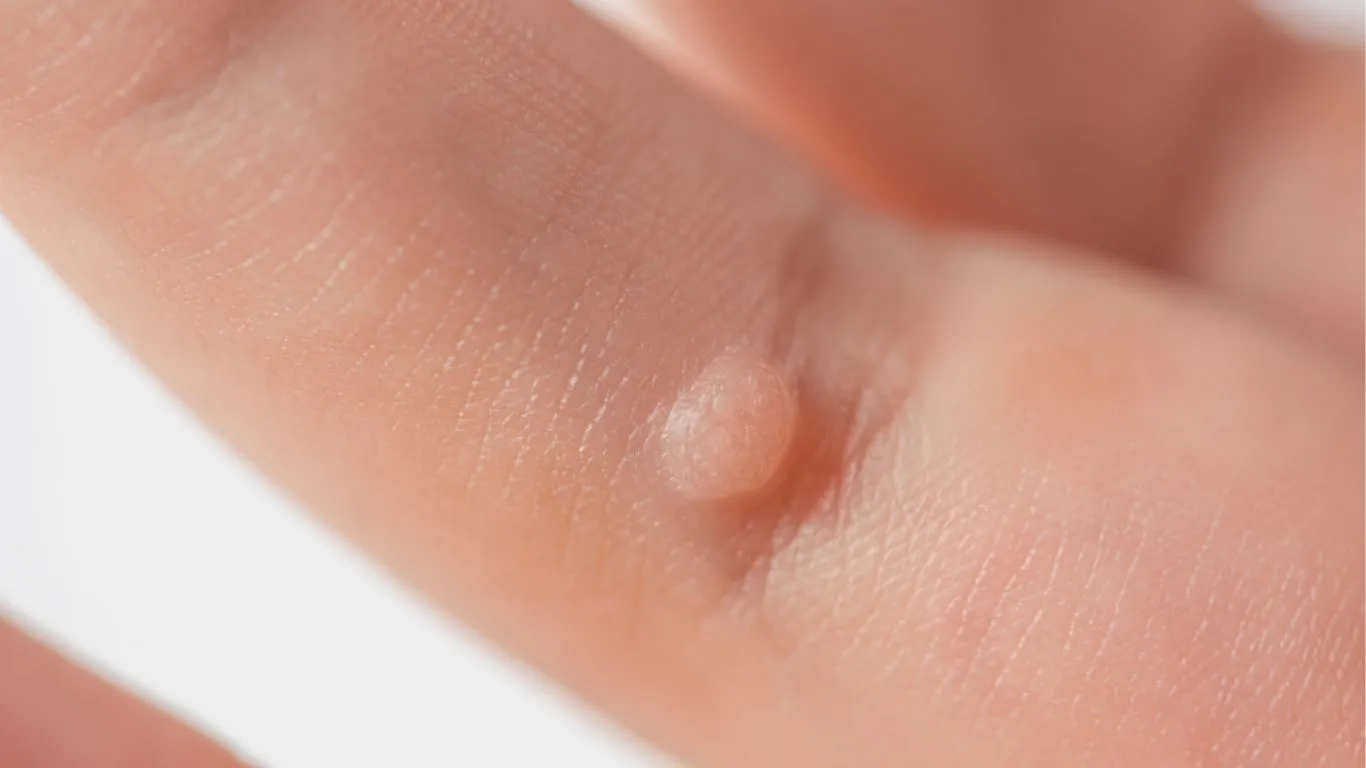
Warts are non-cancerous growths or skin protrusions caused by viral infections, particularly human papillomavirus (HPV). They typically appear on the surface of the skin. Although they are not dangerous, they can be aesthetically bothersome. The types of warts vary according to their location and characteristics, as well as the treatment options available.
Types of Warts
Types of warts include:
Common Warts
Often appear on the hands, fingers, and knees.
Characterized by a rough surface and brown or gray color.
Can be small or large and are usually painless.
Plantar Warts
Found on the soles of the feet and can cause pain when pressed.
Rough, flat, and hard with a black center, indicating small bleeding beneath the skin.
Flat Warts
Can appear anywhere on the body and are small and flat with smooth patches.
Usually skin-colored or pink, often occurring in groups, and are common in children and young adults.
Genital Warts
Located in the genital area for both men and women, often grayish in color.
Require medical consultation for appropriate treatment as they can increase the risk of cancer in the affected area.
Can be prevented through the HPV vaccine.
Causes of Warts
Some strains of HPV cause wart. The virus can enter the skin through small cuts, leading to abnormal cell growth. As a result, the outer layer of skin thickens and hardens, forming warts. They typically affect moist and soft skin or damaged areas.
Is this condition contagious?
Yes, warts are contagious and can spread through direct or indirect contact. Direct contact occurs when touching another person’s wart or skin-to-skin contact. Indirect contact includes using contaminated items like towels or razors.
Read More: Hives (Urticaria)
Treatment of Warts
Warts often disappear on their own but can take one to two years. However, because they can spread, cause pain, and affect daily life, a doctor may recommend treatment. Available options include:
Topical Products
Some wart treatments contain salicylic acid, which gradually dissolves wart layer by layer.
These products come in liquid, gel, or patch form and may need daily application for several months, with recovery rates of 50% to 70% for common warts.
Freezing
Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze the wart, resulting in its destruction.
Cauterization
Thermal cautery is a medical procedure used to destroy the wart by applying high heat, typically using an electric device to heat a metal tip.
Laser Treatment
Can be used to remove warts that do not respond to traditional treatments. The doctor uses laser light to heat and destroy small blood vessels inside the wart, cutting off its blood supply, which kills the wart. This may cause scarring.
Can I Remove a Wart at Home?
It is not advisable to attempt to remove a wart at home, as this can worsen the infection and spread the wart to other areas. Consulting a doctor for appropriate treatment is recommended.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing this condition, follow these steps:
- Avoid touching another person’s wart.
- Do not share personal items; avoid using towels, clothes, nail tools, or razors with others.
- Avoid biting your nails or excessive touching of the skin. Keep your skin moist to prevent dryness and cracks, as the virus can enter through cracked skin.
- Consult your doctor about the HPV vaccine, which is typically given to children and young adults.
- Wear appropriate footwear, like sandals or shoes, in public changing rooms or swimming pools.
- If you have a wart, follow these tips to limit its spread:
- Use a bandage to cover the wart.
- Do not scratch or cut the wart.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after touching it.
- Do not shave over the wart.
- Keep your feet dry to prevent the spread of plantar warts.
References:
- MSD Manuals. (2024, January 9). Quick Facts:Wart- MSD Manual Consumer Version. MSD Manual Consumer Version. https://www.msdmanuals.com/home/quick-facts-skin-disorders/viral-skin-infections/warts
- Wart. (2024, May 1). Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15045-warts